| Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD)
What is it?
The
MACD is one of the most popular oscillator used by currency traders.
This is a momentum indicator can be used to confirm trends, while also
indicating reversals, or overbought/oversold conditions. The MACD is
calculated by taking the difference between the 2 exponential moving
averages. The two that is usually used are the 26-day and 12-day moving
averages.
How can MACD be used for trading?
Crossovers
The
most common way to use the MACD is to buy/sell a currency pair when it
crosses the signal line or zero. A sell signal occurs when the MACD
falls below the signal line, while a buy signal occurs when the MACD
rallies above the signal line.
Overbought/Oversold
The
MACD can also be used as an overbought/oversold indicator. When the
shorter moving average moves away significantly from the longer moving
average (i.e., the MACD rises), it is likely that the currency price’s
movements are starting to exhaust and will soon return to more
realistic levels.
Divergences
When
the MACD diverges from the trend of the currency price, this may signal
a trend reversal. In addition, if the MACD makes a new low while the
currency pair does not also make a new low, this is a bearish
divergence, indicating a possible oversold condition. Alternatively, if
the MACD is making new highs while the currency pair fails to confirm
these highs, this is a bullish divergence, indicating a possible
overbought condition.

Stochastics
What is it?
The
stochastic oscillator is a commonly used momentum indicator that
measures the current currency price compared to its historical price
for a given time period. It looks to gage the strength and momentum of
a currency pair's price action by measuring the degree by which a
currency is overbought or oversold. The scale for the indicator is 0 to
100. Readings above 80 indicate overbought conditions, as it reflects
the fact that the currency is strong and the price is closing near the
high of the trading range. Readings below 20 indicate oversold
conditions and reflects the fact that the currency is weak and is
closing near the low of the trading range.
How can stochastics be used for trading?
Detect Overbought and Oversold Conditions
The
most common way to analyze stochastics is to sell when the reading is
above 80, which implies overbought conditions and to buy when the
reading is below 20, which implies oversold conditions.
Divergence
Buy
and sell signals can also be given when stochastics show divergence,
indicating a possible trend reversal. Divergence occurs when the
stochastic values are moving in one direction and the price values are
moving in the opposite direction.

Relative Strength Index (RSI)
What is it?
The
relative strength index or RSI is probably the most popular oscillator
used by the FX trading community. It was developed by J. Welles Wilder
Jr. to gage the strength or momentum of a currency pair. This indicator
is calculated by comparing a currency pair’s current performance
against its past performance, or its up days versus its down days. RSI
is on a scale of 1-100, where any point above 70 is considered
overbought, while any point below 30 is considered oversold. The
standard time frame for this measure is 14 periods, although 9 and 25
periods are also commonly used. Generally, more periods tend to yield
more accurate the data.
How Can RSI be Used for Trading?
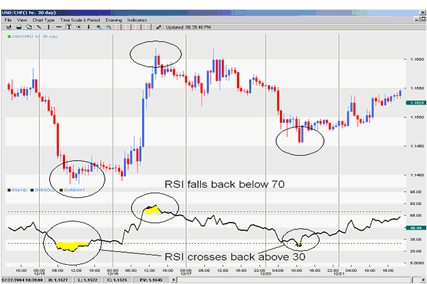
RSI Can be Used to Identify Extreme Conditions or Reversals.
RSI
above 70 is considered overbought and indicating a sell signal. RSI
below 30 is considered oversold which would imply a buy signal. Some
traders identify the long-term trend and then use extreme readings for
entry points. If the long-term trend is bullish, then oversold readings
could represent potential entry points.
RSI Can be Used to Indicate Divergence
Trade
opportunities can also be generated by scanning for positive and
negative divergences between the RSI and the underlying currency pair.
For example, a falling currency pair where RSI rises from a low point
of 15 back up to 50. With RSI, the underlying pair will often reverse
its direction soon after such a divergence. Consistent with this
example, divergences that occur after an overbought or oversold reading
usually provide more reliable signals.
Bollinger Bands
What is it?
Bollinger
bands are very similar to moving averages. The bands are plotted at two
standard deviations above or below the moving average. This is
typically based off of the simple moving average, but an exponential
moving average can be used to increase the sensitivity of the
indicator. A 20-day simple moving average is recommended for the center
band and 2 standard deviations for the outer bands. The length of the
moving average and number of deviations can be altered to better suit
trader preferences and volatility of a currency pair. In addition to
identifying relative price levels and volatility, bollinger bands can
be combined with price action and other indicators to generate signals
and be a precursor to significant moves.
How can Bollinger Bands be Used for Trading?
Bollinger
bands are typically used by traders to detect extreme unsustainable
price moves, capture changes in trend, identify support/resistance
levels and spot contractions/expansions in volatility. There are a
number of ways to interpret Bollinger Bands.
Breakouts
Some
traders believe that when the prices break above or below the upper or
lower band, it is an indication that a breakout is occurring. These
traders will then take a position in the direction of the breakout.
Overbought/Oversold Indicators
Alternatively,
some traders use Bollinger Bands as an overbought and oversold
indicator. As shown in the chart below, when the price touches the top
of the band, traders will sell, assuming that the currency pair is
overbought and will want to revert back to mean or the middle moving
average band. If the price touches the bottom of the band, traders will
buy the currency pair, assuming that it is oversold and will rally back
towards the top of the band. The spacing or width of the band is
dependent on the volatility of the prices. Typically, the higher the
volatility, the wider the band and the lower the volatility, the
narrower the band.

Pulling it All Together Alone, none of these indicators yield great
results. However, when combined and used in unison, they can give
traders the extra edge needed to better understand short term trading
dynamics. Therefore it is important for traders to look for
relationships between the different indicators as multiple signals can
provide the most accurate trading predictions.
http://www.aboutcurrency.com/articles/fxtechnical/the_most_popular_indicators_used_in_forex.shtml
| 

